ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND
Speech testing is a critical part of the audiological evaluation and need to be performed according to specific standards. Word discrimination lists are standardized and recorded in many languages including Arabic, such as Dr. Salah Suliman’sand Dr. AbdulazizAshoor’slists, however are not readily available. Difficulty to obtain recorded such materials made the use of recorded monosyllabic word tests is limited in Saudi Arabia compare to live voice. Using monitored live voice leads to unstandardized speech testing protocols, discrepancy in patient’s audiological evaluation, inconsistent test results and outcomes
OBJECTIVE
This pilot study aims to provide a phonemically balanced and recorded monosyllabic Arabic speech discrimination materials (KAU list) to
–Reliably evaluate patient’s speech discrimination ability
–Standardize speech discrimination test protocols across clinics
–Eliminate discrepancy in audiological evaluation and patient’s outcome
METHODS
Six phonemically balanced wordlists were constructed. Word familiarity was determined using a survey to select 150 words then recorded using a professional female voice. Nine normal hearing subjects participated in the study to produce articulation curves for each list.
RESULTS
Articulation curves obtained were in agreement with previously published articulation curves in Arabic and other foreign languages, which monosyllabic words lists were used in similar test conditions.
CONCLUSIONS
The proposed wordlists agree with previously published Arabic wordlists for measuring speech discrimination skills of Arabic speaking individuals.
Apr 2016
AudiologyNow
METHODS
Words Selection
Two hundred monosyllabic words were extracted from five articles published in three local journals in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, representing words used for reporting national and international news.
Using surveymonkey.com, 46 subjects participated in a survey to assess word familiarity. Words that received a score of 85% or more in scale of Familiarity were included in the study.
Finally, 150 words were selected to construct six twenty-five wordlists.
Words Recording
Lists were recorded using a female voice using a digital stereo condenser microphone MV88 connected to iPhone 6s in a double-wall sound proof booth. Each word was recorded three times.
Words were transferred to Garageband software on a MAC computer for editing.
List Structure and Balance
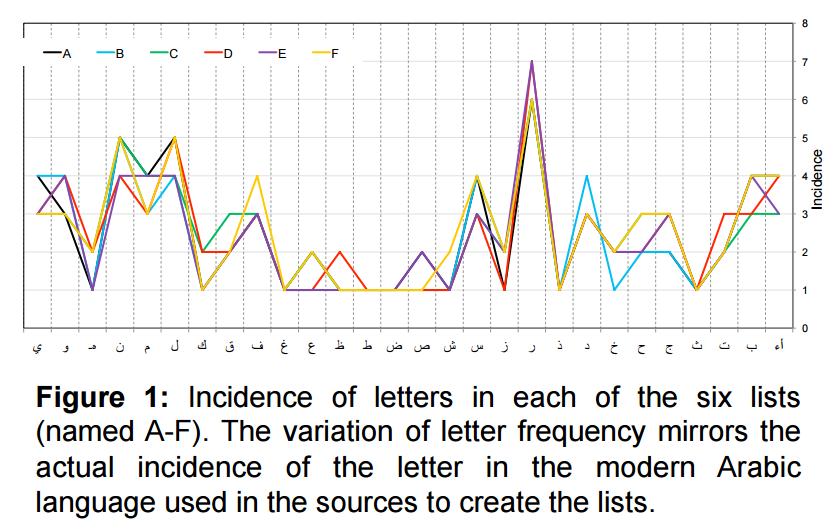
Each list was designed to have at least one of the 28 Arabic letters.
Letters were extracted from each word and counted.
Finally, six lists were designed to have the same number of each of the alphabet letters +/- one.
Six lists were created and were phonemically balanced.
Data Collection and Validation
Nine normal hearing adults participated in this pilot study.
Lists were presented at 10 dBHL and increased in 10 dBHL increments until the
the subjects scored 100% correct.
RESULTS

CONCLUSIONS
The proposed wordlists agree with previously published Arabic wordlists for measuring speech discrimination skills of Arabic speaking individuals
|